Management Training: Problem Solving Skills
If you are a manager, then you need to be a problem solver. The life of a manager is full of problems to solve. Your task, as a manager, is to solve problems quicker than they crop up. If you have this process the wrong way round, if problems crop up at a rate that is faster than you can solve them, then your problems pile up and your progress stops. Therefore problem solving is one of the master skills of management.
Three categories of problem solving
There are three fundamental aspects to problems solving:
- Problem prevention: this means pre-empting the problem and stopping it before it even has time to happen. Prevention is the best form of problem solving.
- Problem, cause, solution: this means analysing the causes of problems and interrupting or eliminating the causes that are feeding and maintaining the problem state. If the causes of the problem are identified and removed, the problem state should cease to exist.
- Problem, implication, countermeasure: This means analysing the implications of an existing problem and taking countermeasures to reduce the negative effects of the existing problem. Note that problem implication countermeasure also contains within it, elements of problem prevention; meaning that if you have problem A already, then the existence of problem A may have potential to create a second problem B that could be worse than problem
For example, if you had a broken leg in plaster, then we could call that "problem A".
Then, if you were to get on an aeroplane for a long haul flight to Australia, with a leg in plaster, that combination could lead to a deep vein thrombosis (D.V.T.) which could be your next, VERY serious "problem B".
1. Problem prevention. Scanning the situation
So your brain should be scanning the situation and asking:
What are the likely problems that could occur?
Without being negative or depressed, you must expect things to go wrong. Putting it the other way, don't expect all your plans to work out as planned.
Why do your plans not work out the way you visualised them?
Answer: because your plans were built by human beings who don't have access to all the knowledge and even if you did have all the knowledge of the current situation, the situation is in a state of flux, and will be different tomorrow.
So expect unexpected things to happen.You need not be surprised when you get stuck behind a slow moving tractor, which delays you for your meeting by 20 minutes. Don't blame your lateness on the tractor. Blame your lateness on the fact that you failed to take account of the unpredictable predictable problem.
On one level the tractor was unpredictable. But on another more general level you can be pretty certain that something will go wrong during the day. Your job is to build into your plan, a certain level of expectation of problems. And if you can use your imagination and intelligence you may even be able to predict the "unpredictable-event" and take evasive action before the problem manifests itself.
2. Problem, cause, solution
Whenever you have a problem you need to draw the problem cause solution mind map and fill it in.
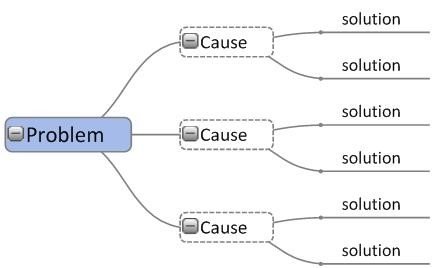
Name the problem, name three major causes of the problem and name the 6 possible best solutions for the three major causes. Enact the best three solutions and the problem should be solved.
3. Problem implication and countermeasure
If you really want to go-to-town on problem solving then get accustomed to thinking in terms of the following mental image. Whenever problems arise, which is every day, then either draw this shape out for others to see, or think of this shape in your mind's eye, and begin to fill in the details.
Name the problem A.
Find the main causes of A.
Write down the 6 solutions to A.
Then think of the possible problematic implications of A, which would be possible problems in their own right.
Write down the 6 countermeasures that would need to be set in place to forestall the implied problems B,C and D.
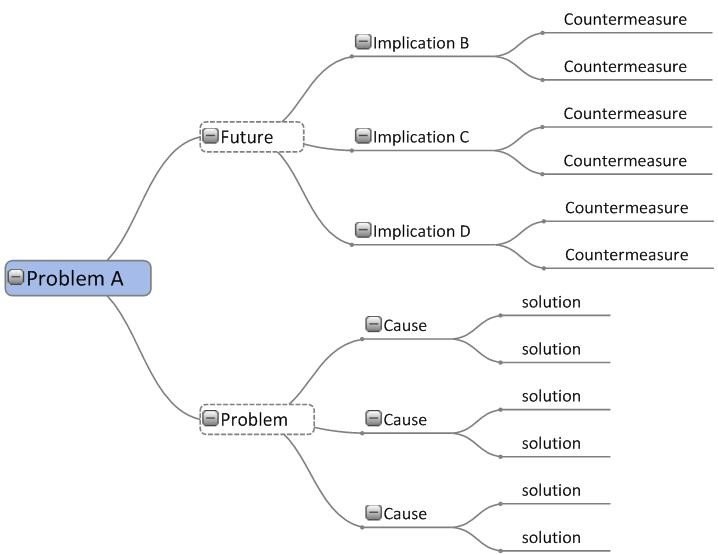
If you did what we are suggesting here, and even better, if you got your whole team together and did the analysis together according to the above diagram, can you imagine how interesting and beneficial that could be?
Go for it!
Definition: Problem-Cause-Solution method
The Problem-Cause-Solution method is a business tool that guides a manager through four clear steps: name the problem, list the main causes, create many fixes for each cause, then act on the best fixes. By linking every action to a known cause, the method removes the root of the issue rather than masking its signs.
Show CG4D Definition
- Starts with a clear statement of the single problem to be solved
- Investigates and records at least three direct causes of that problem
- Generates several possible fixes matched to each named cause
- Selects and applies the strongest fixes to remove the causes and end the problem
Article Summary
A great manager stops trouble before it starts, digs to the root when it appears, and blocks knock-on risks; use these three moves to beat problems faster than they arrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some questions that frequently get asked about this topic during our training sessions.
What is problem prevention and why is it the best form of problem solving?
How can a manager scan for likely problems during daily work?
What are the four steps in the Problem-Cause-Solution method?
Why draft six solutions for every cause you list?
How does considering implications and countermeasures limit problem impact?
When should I involve the whole team in problem analysis?
What are quick problem solving tips for managers working under time pressure?
Thought of something that's not been answered?
Did You Know: Key Statistics
A 2024 CIPD Learning at Work survey shows 68% of UK line managers say they need stronger problem solving and root cause skills. McKinsey’s 2023 study of 1,200 teams finds those that follow a clear problem-solving method meet project deadlines 30% more often.Blogs by Email
Do you want to receive an email whenever we post a new blog? The blogs contain article 5-10 minutes long - ideal for reading during your coffee break!
Further Reading in Leadership and Management
-
What is Human Nature?
Discover six traits of human nature-ego, purpose, reason, emotion, pattern seeking and smart laziness-and use them to predict, influence and motivate people.
Read Article > -
Achieving Goals, Not Just Tasks
Shift your team from task ticking to goal achievement. Learn how praise, profit share, career growth and training create rewards that ignite employee drive.
Read Article > -
Managing Imposter Syndrome
Learn practical ways for managing imposter syndrome, restore self-belief and align inner feelings with action to turn self-doubt into steady confidence.
Read Article > -
How Can We Improve Leadership?
Improve leadership fast with seven key skills: clear vision, sharp communication, team building, conflict resolution, motivation and role-model action.
Read Article > -
Five Common Management Mistakes
Learn to avoid common management mistakes by setting goals, ranking tasks, delegating, speaking with respect and guiding performance via practical training.
Read Article >
Looking for Leadership and Management Training?
If you're looking to develop your Leadership and Management Skills, you may find this Leadership and Management Training Course beneficial:
Open Training Course Pricing and Availability
Next Open Course Running tomorrow in Leeds City, places available







